SPEVIGO® (spesolimab) safety profile

SPEVIGO®(spesolimab)
SPEVIGO® (spesolimab) has a favourable benefit-risk profile1,2
|
-
*
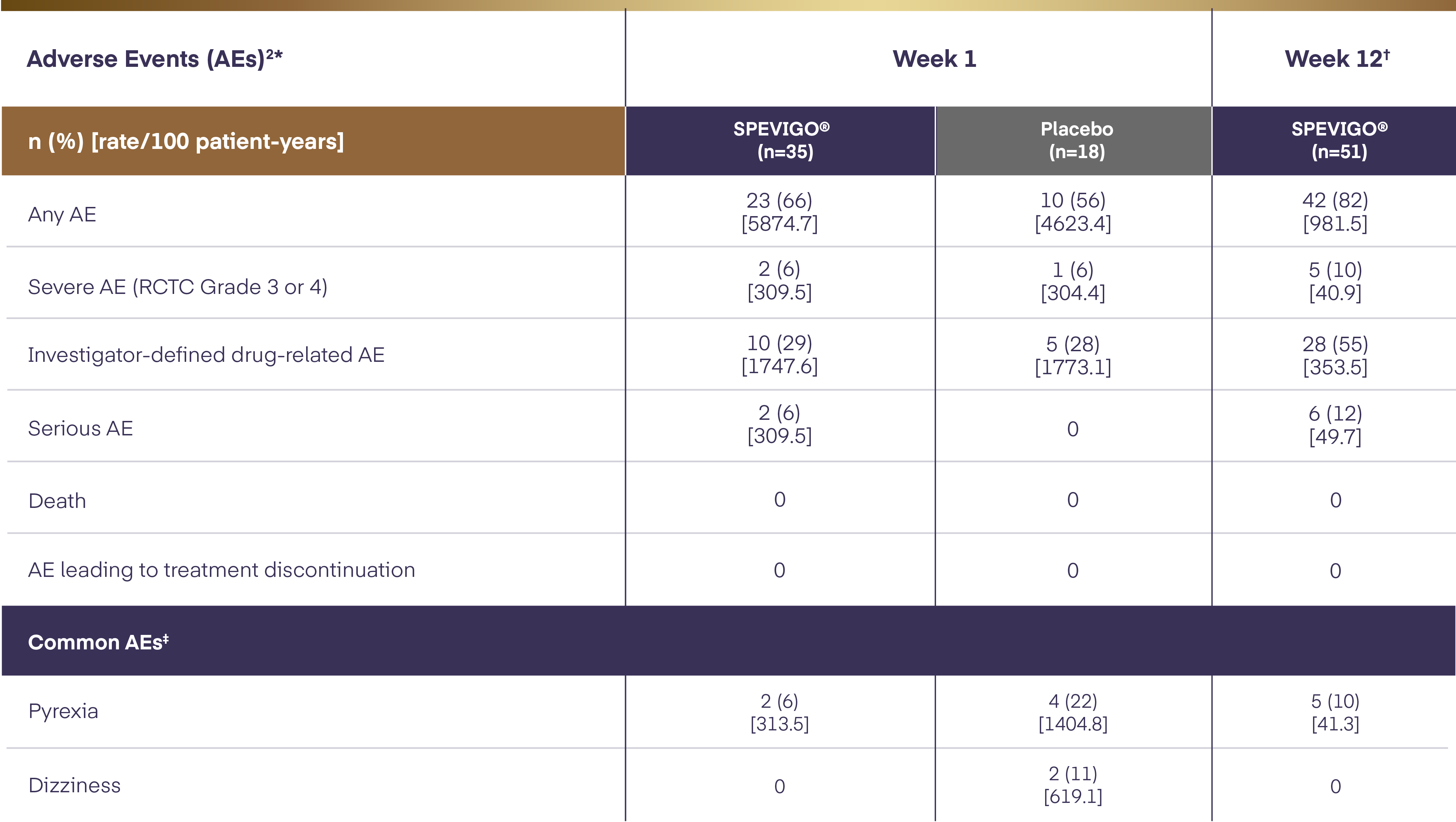
All AEs occurring between the start of treatment and end of the residual effect period (16 weeks after the placebo dose or last dose of SPEVIGO®. AEs were coded using the Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities (MedDRA) v23.1. AE severity was graded according to the RCTC v2.0. Pustular psoriasis was excluded as an AE from this safety analysis.2
-
†
Data set at Week 12 included patients randomised to SPEVIGO® (spesolimab) who received up to 3 doses of SPEVIGO® (spesolimab) and patients randomised to the placebo group who received OL SPEVIGO® (spesolimab) at or after Day 8. All AEs in the residual effect period are included but censored at the day rescue treatment with SPEVIGO® (spesolimab) was administered.2
-
‡
Common AEs are reported in ≥10% of patients in any treatment group.2
Safety through Week 122
The time-adjusted incidence rates of adverse events in patients who received at least 1 dose of SPEVIGO® (spesolimab) decreased from Week 1 to Week 12.
SPEVIGO® Summary of adverse reactions1,2
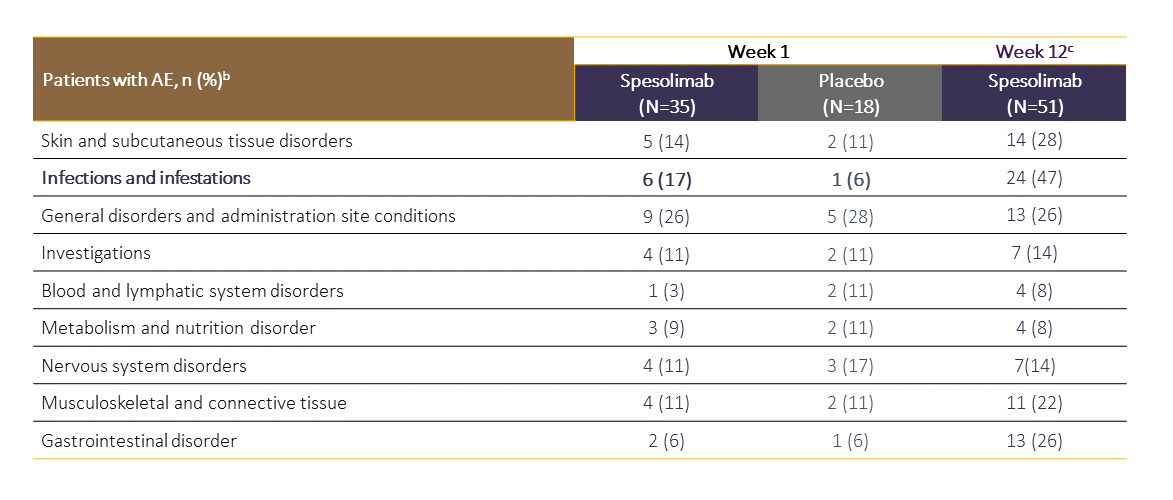
SPEVIGO® may increase risk of infections. During the 1-week placebo-controlled period in the EffisayilTM 1 trial, infections were reported in 17.1% of patients treated with SPEVIGO® compared with 5.6% of patients treated with placebo.1
b AEs that occurred between the start of spesolimab or placebo administration and the end of the residual-effect period (16 weeks after last dose of treatment).
c Dataset at Week 12 includes patients randomized to spesolimab and patients initially randomized to placebo who received open-label spesolimab at Day 8.
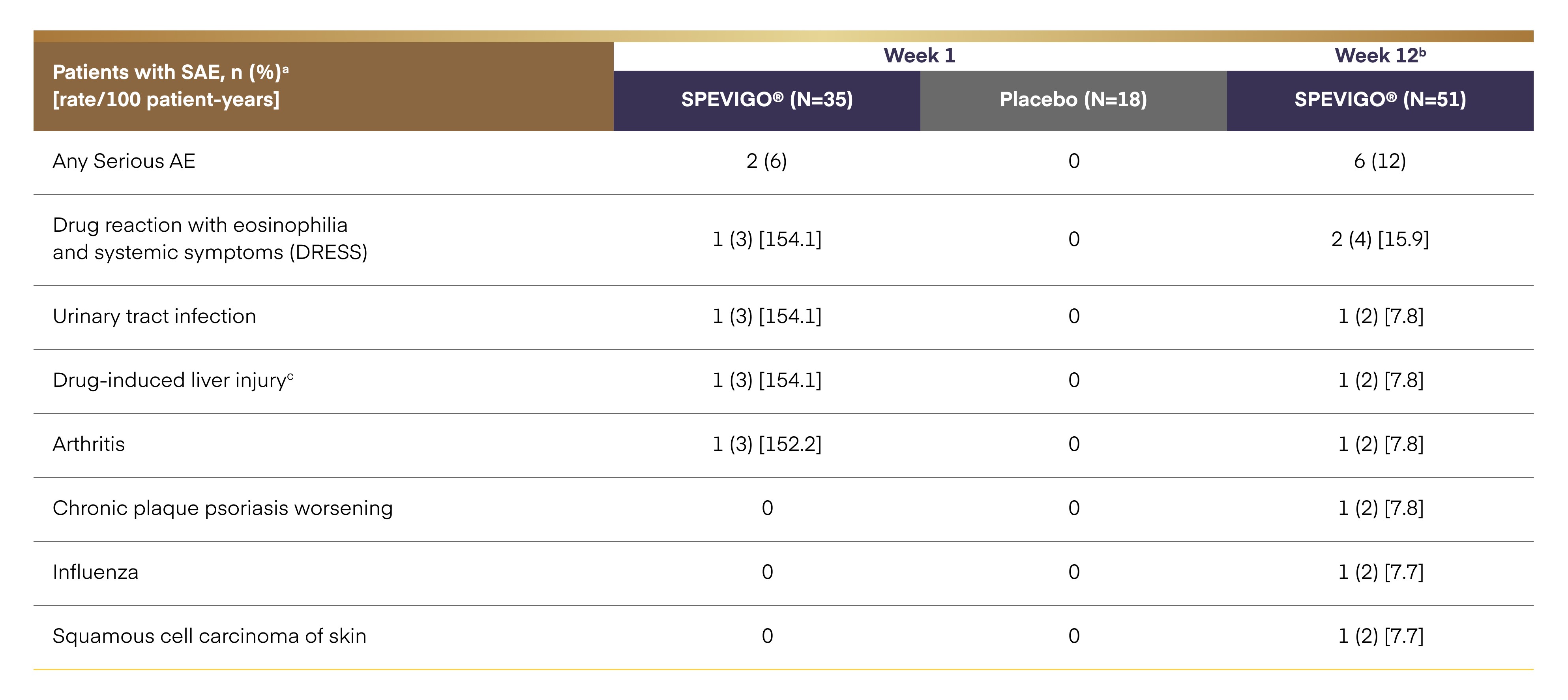
Serious adverse events2
|
a AEs that occurred between the start of spesolimab or placebo administration and the end of the residual-effect period (16 weeks after last dose of treatment). b Dataset at Week 12 includes patients randomized to spesolimab and patients initially randomized to placebo who received open-label spesolimab at or post Day 8. c Reflected by an increase of transaminases and was considered a systemic symptom of DRESS.
References
-
SPEVIGO® Summary of Product Characteristics. Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc; 2022.
-
Bachelez H et al. N Engl J Med. 2021;385(26):2431-2440. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2111563
GPP (07/2025) PC-GR-102302



