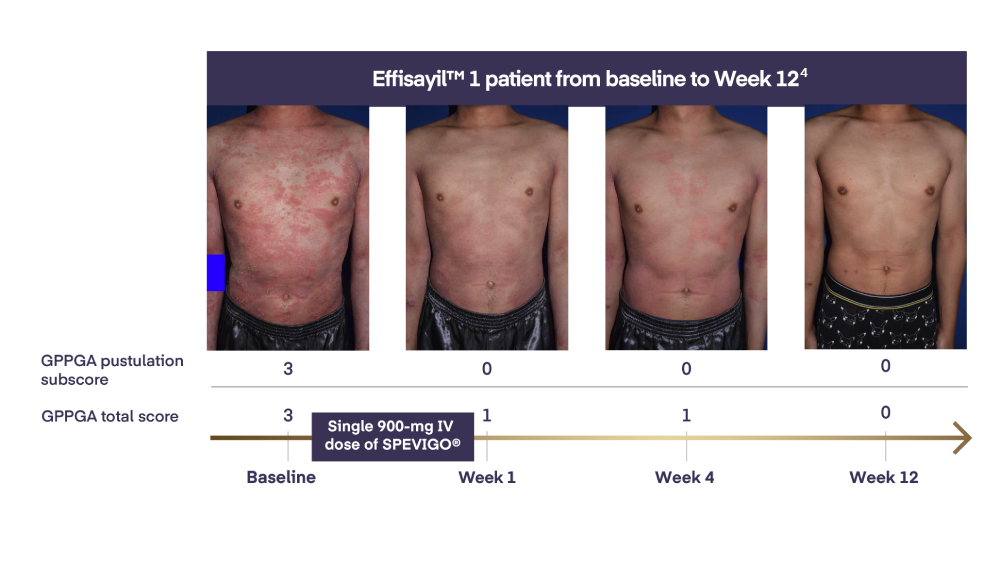
54.3% of patients achieved complete pustular clearance* at Week 11,2

SPEVIGO® (spesolimab)
With SPEVIGO® (spesolimab), 54.3% of patients achieved complete pustular clearance* at Week 11,2
Rapid pustular and skin clearance at Week 11,2
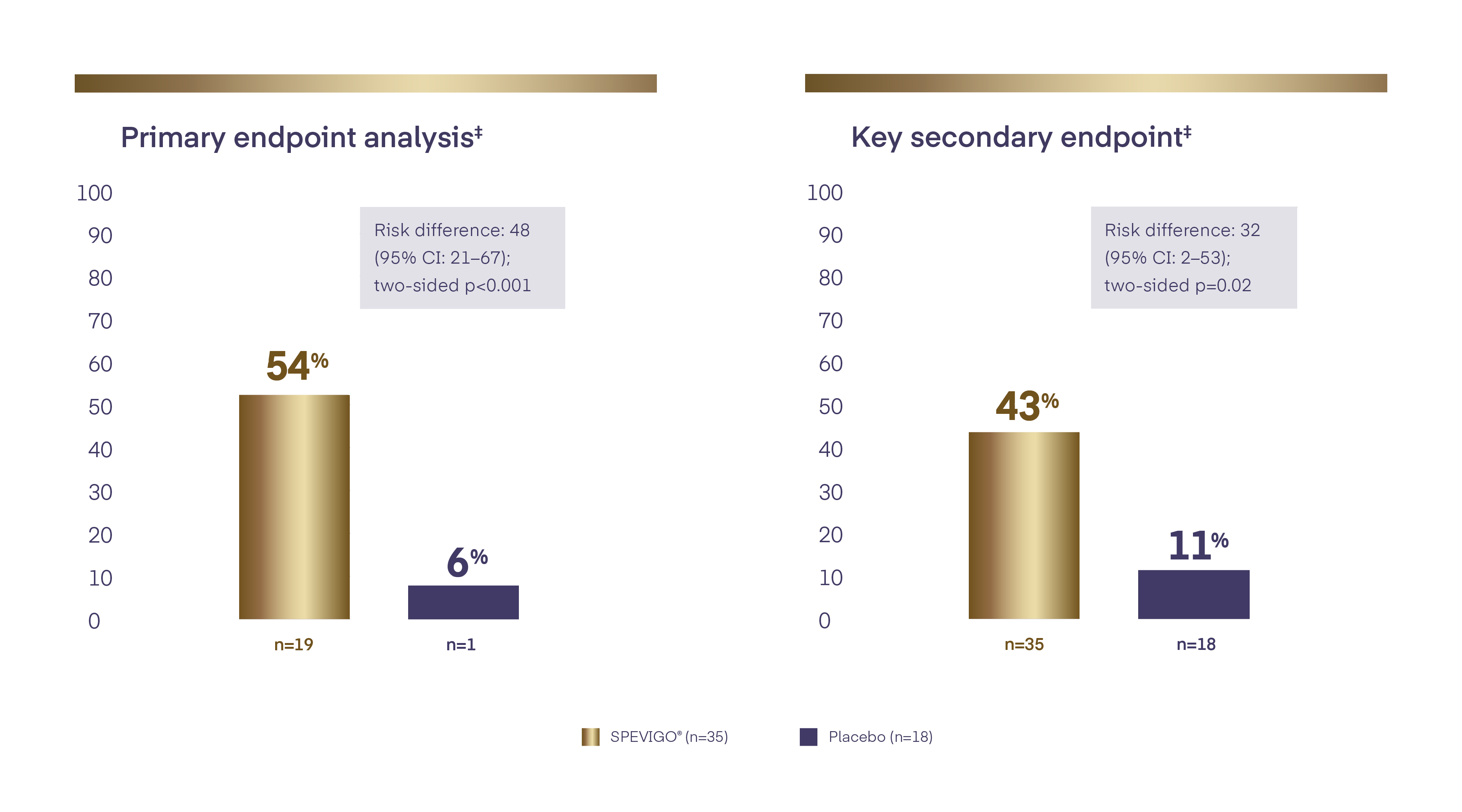
*Pustular clearance defined as GPPGA pustulation subscore of 0 (no visible pustules).1
†Data include all observed cases regardless of any other GPP medication used within the first week.2
‡Missing values or any use of other medication for GPP within the first week of the trial was regarded as non-response for the analysis of the endpoint.2
CI=confidence interval; GPP=Generalized Pustular Psoriasis; GPPGA=Generalized Pustular Psoriasis Physician Global Assessment.
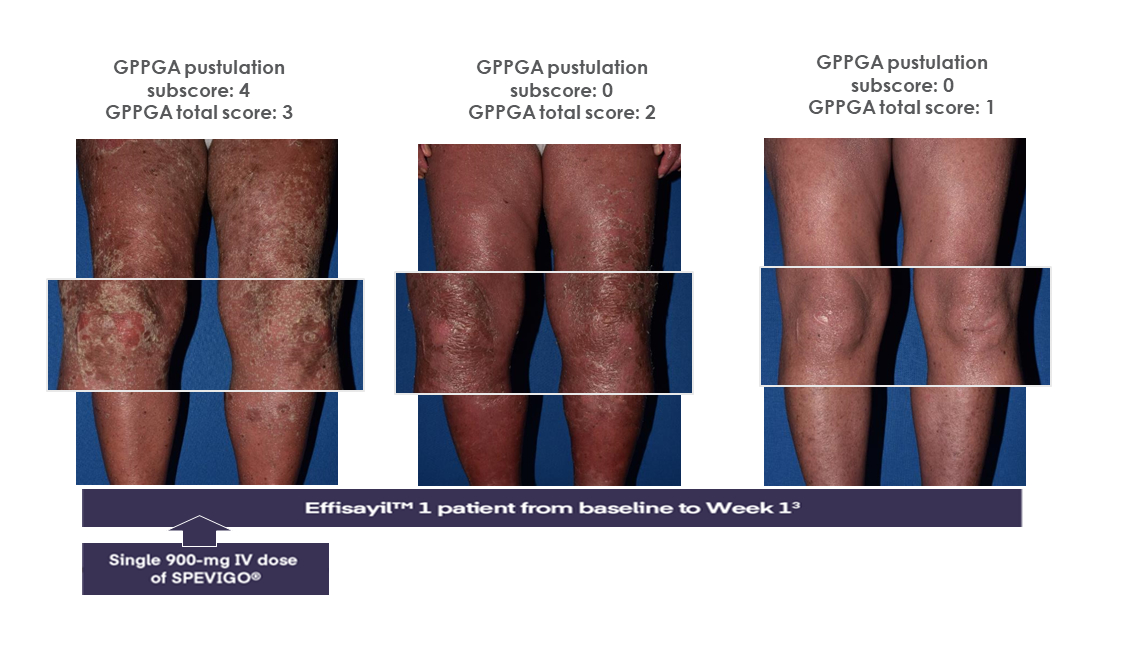
SPEVIGO® delivered complete pustular clearance* in 54.3% of patients at Week 11-3
In Effisayil™ 1, pustular clearance¶ was sustained with SPEVIGO® (spesolimab) for the 12-week study period2
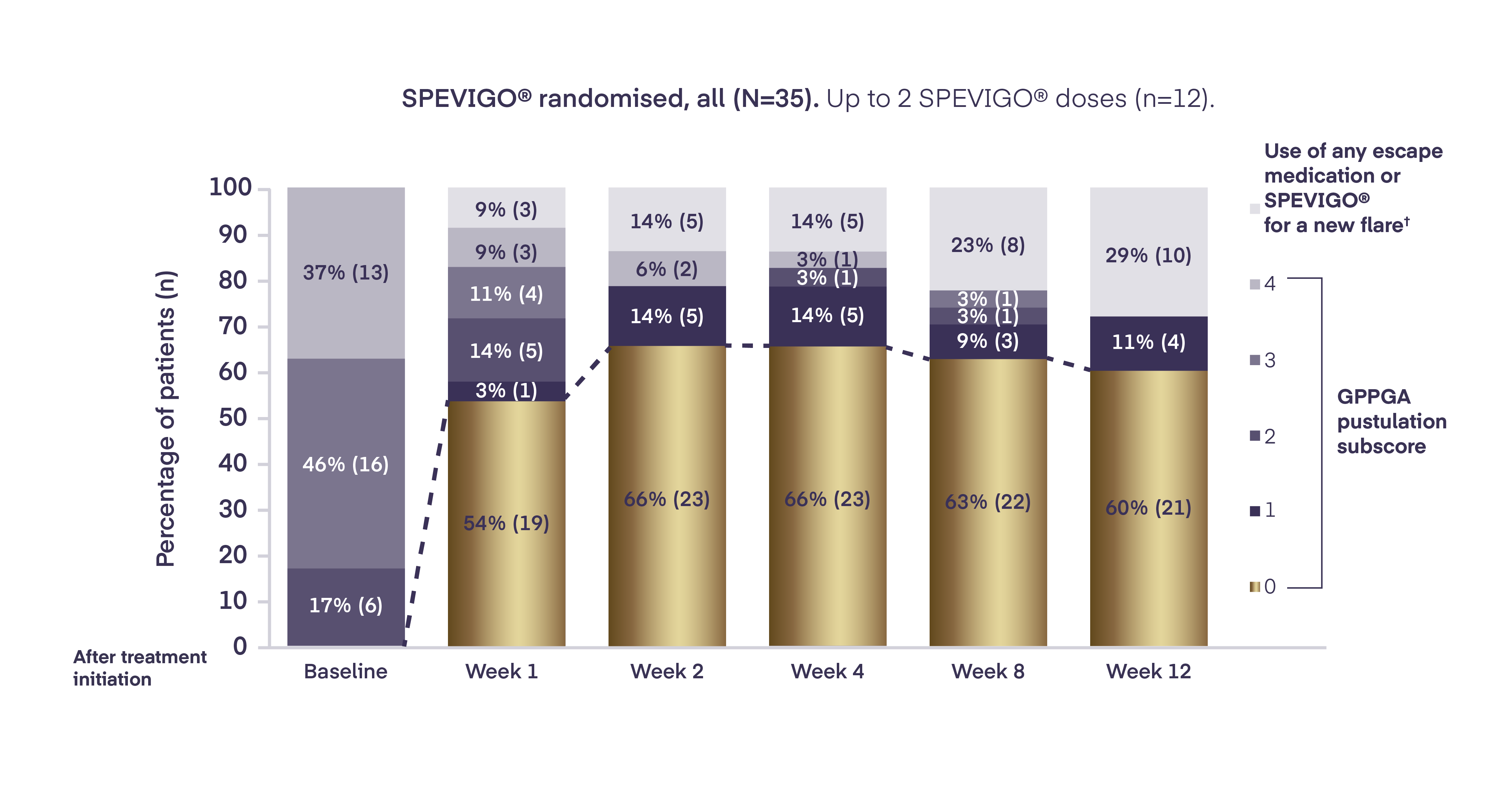
¶ Pustular clearance defined as GPPGA pustulation subscore of 0 (no visible pustules).1
# Defined as an increase of ≥2 points in both the GPPGA total score and the pustulation subscore after a GPPGA total score of 0 or 1 had been reached.2
In Effisayil™ 1, flare control** was sustained with SPEVIGO® (spesolimab) for the 12-week study period2
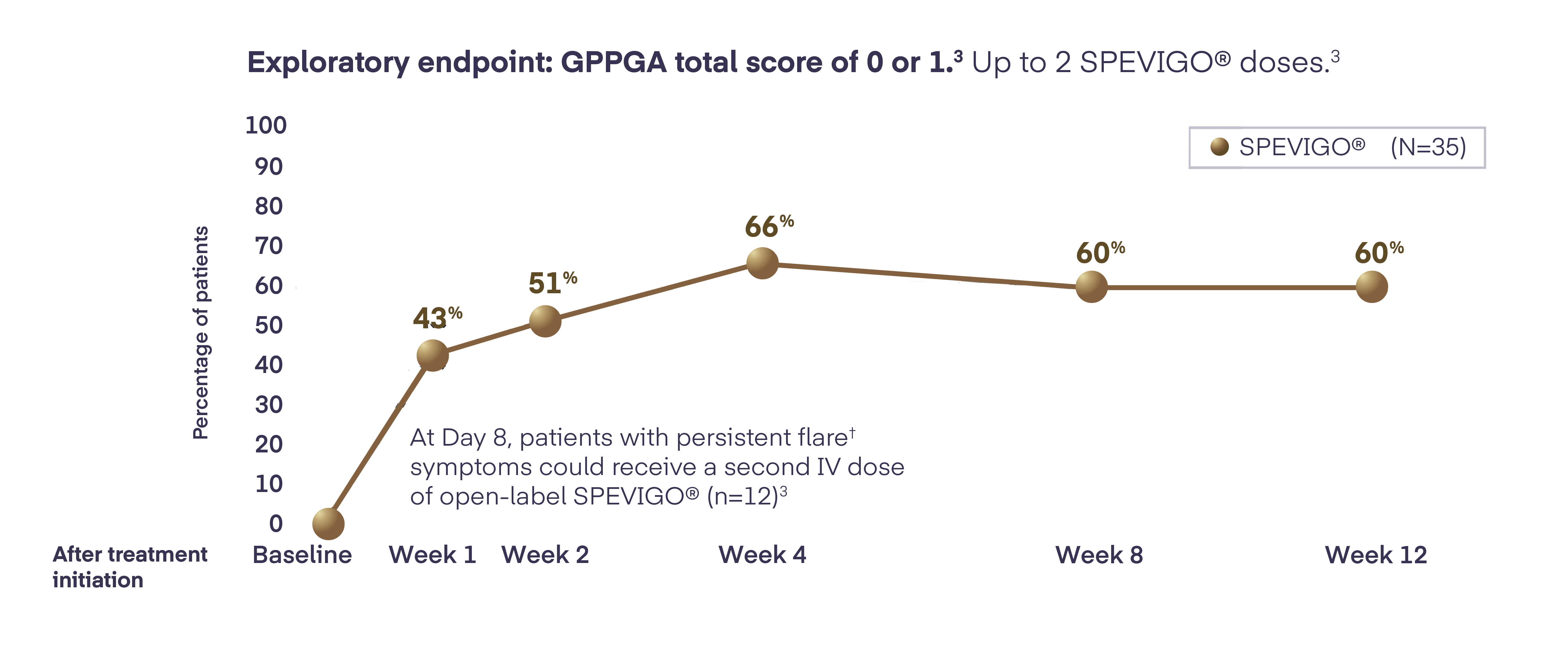
** Flare control defined as GPPGA total score of ≤1 and was reported for the 12-week study period.2
†† Persistent flare defined as ≥2-point GPPGA total score and ≥2-point GPPGA pustulation subscore.2
In Effisayil™ 1, flare control was sustained with SPEVIGO® (spesolimab) for the 12-week study period2
References
-
SPEVIGO® Summary of Product Characteristics. Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH.
-
Bachelez H et al. N Engl J Med. 2021;385(26):2431-2440. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2111563
-
Strober B et al. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2021;11(2):529-541. doi:10.1007/s13555-021-00493-0
-
Burden AD, et al. Br J Dermatol, Volume 189, Issue 1, July 2023, Pages 138–140. Accessed June 13, 2024. https://academic.oup.com/bjd/article/189/1/138/7131301#supplementary-data Figure, pg.10
-
Rentz AM et al. J Dermatolog Treat. 2020;31(5):460-469. doi:10.1080/09546634.2019.1709612
-
Gould D et al. J Clin Nurs. 2001;10(5):697-706. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2702.2001.00525.x
GPP (07/2025) PC-GR-102302



